Unlocking the Magic of ChatGPT: A Journey Through Transformer-Based Language Models
Published:
Imagine an AI that crafts poetry, debugs code, and explains quantum physics—all while adapting to your unique conversational style. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the reality of ChatGPT, a pinnacle achievement in modern AI. But how does it really work? The secret lies in a revolutionary architecture called the Transformer. In this deep dive, we’ll demystify Transformers, build a Shakespeare-generating model from scratch, and reveal what powers ChatGPT’s linguistic brilliance.
Why Understanding AI Matters Now More Than Ever
AI isn’t just a tool—it’s an economic catalyst and societal force multiplier. Systems like ChatGPT showcase the staggering potential of machines that understand and generate human language. Yet their probabilistic nature (different responses to identical inputs) underscores why we must peek under the hood. Grasping these foundations empowers us to harness AI ethically and creatively—fueling global innovation.
The Transformer Revolution: “Attention Is All You Need”
In 2017, a landmark paper dismantled decades of NLP dogma. Before Transformers, models processed text sequentially (left-to-right), struggling with long-range context. Transformers replaced this with self-attention: a mechanism letting every word dynamically “attend” to relevant words elsewhere in the sentence.
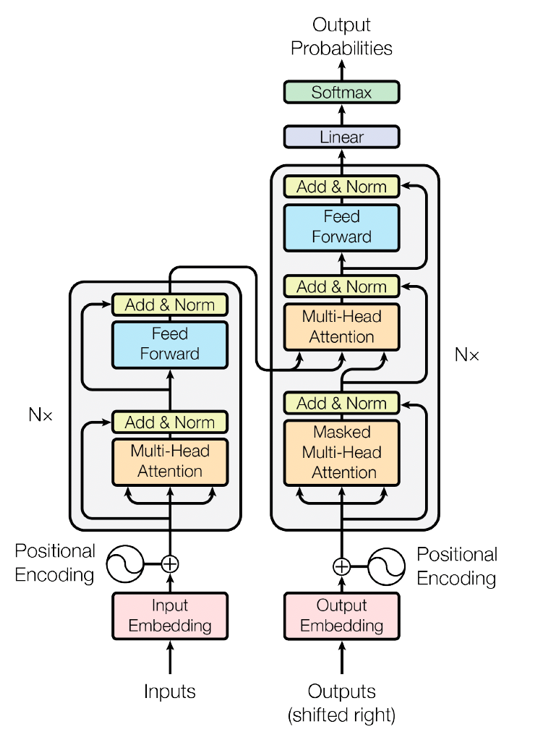
Think of it as a room of experts debating a topic. Each expert (word) listens to others, weighs their relevance (attention scores), then synthesizes collective insight. This parallel processing unlocked unprecedented language understanding—becoming the backbone of ChatGPT, BERT, and beyond.
Building a Shakespearean Transformer: From Data to Deployment
To make this tangible, we built a simplified Transformer trained on Shakespeare’s complete works. Here’s how it works:
1. Data Preparation: The Art of Tokenization
- Raw text is split into characters (e.g., “A” → 65, “!” → 33)
- Data splits: 90% for training, 10% for validation (to catch overfitting)
- Batch processing: Groups of text snippets trained in parallel for efficiency
2. Model Architecture: Decoder-Only Design
Our model mirrors GPT’s decoder-only structure. Key components:
- Self-Attention Block: Tokens “vote” on each other’s relevance via query, key, and value vectors
- Triangular Masking: Ensures tokens only see prior words (critical for text generation)
- Multi-Head Attention: Runs 4+ attention operations in parallel, capturing nuanced relationships
- Feed-Forward Networks: Processes each token independently post-attention
- Residual Connections + LayerNorm: Stabilizes training and gradients
# PyTorch pseudo-code for self-attention
queries = W_q * embeddings # What am I looking for?
keys = W_k * embeddings # What do I contain?
values = W_v * embeddings # What should I output?
attention_scores = (queries @ keys.T) / sqrt(head_size)
attention_scores = masked_fill(attention_scores, upper_tri=True, value=-inf)
weights = softmax(attention_scores)
output = weights @ values # Context-aware token embeddings
3. Training & Optimization
- GPU Acceleration: Leveraged CUDA for 100x speedups
- Adam Optimizer: Balances fast convergence and stability
- Dropout Regularization (0.2): Randomly “drops” neurons to prevent overfitting
- Scaling Attention: Weights divided by √(head size) to avoid volatile gradients
Training Insights:
- Loss dropped steadily over epochs
- Smaller context windows (e.g., 64 chars) sped up training but limited coherence
- Hyperparameter tuning (embedding dim, batch size) slashed validation loss by 37%
4. Text Generation: Successes and Limitations
The model learned to output Shakespeare-like syntax:
“KING RICHARD III:Shall I survive the dead? What do you here? When that my life was void of your fair eyes?”
But limitations surfaced:
- Character-level tokenization ignored word semantics
- Short context windows fractured long-range dependencies
- Outputs lacked true thematic coherence—highlighting why modern models use subword tokenization and trillion-token datasets
From Toy Model to ChatGPT: The Chasm Bridged
Our Shakespearean Transformer is a microscopic cousin of ChatGPT. Key differences:
| Component | Our Model | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Decoder-only | Decoder-only |
| Training Data | Shakespeare (5MB) | Internet-scale (45+ TB) |
| Tokenization | Characters | Subwords (50k+ tokens) |
| Parameters | ~10M | ~175B |
| Attention Heads | 4 | 96+ |
| Training Hardware | 1 GPU | Thousands of A100 GPUs |
ChatGPT’s training involves two colossal phases:
- Pre-training: Predicts next words on internet text (books, forums, code)
- Fine-tuning: Human feedback refines outputs for safety, accuracy, and alignment
Final Thoughts
Transformers redefined what machines can create. By building one from scratch, we’ve glimpsed the fusion of linear algebra, optimization, and linguistic intuition that powers ChatGPT. As AI evolves, these principles will shape everything from personalized education to real-time translation—propelling us toward a future where language barriers crumble, and creativity amplifies human potential.
The next breakthrough? It might just start with your experiments!
Stay tuned for more amazing blog posts!
References
- Andrej Karpathy Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/@AndrejKarpathy
